5 minute presentation. Unmute for audio explanation.
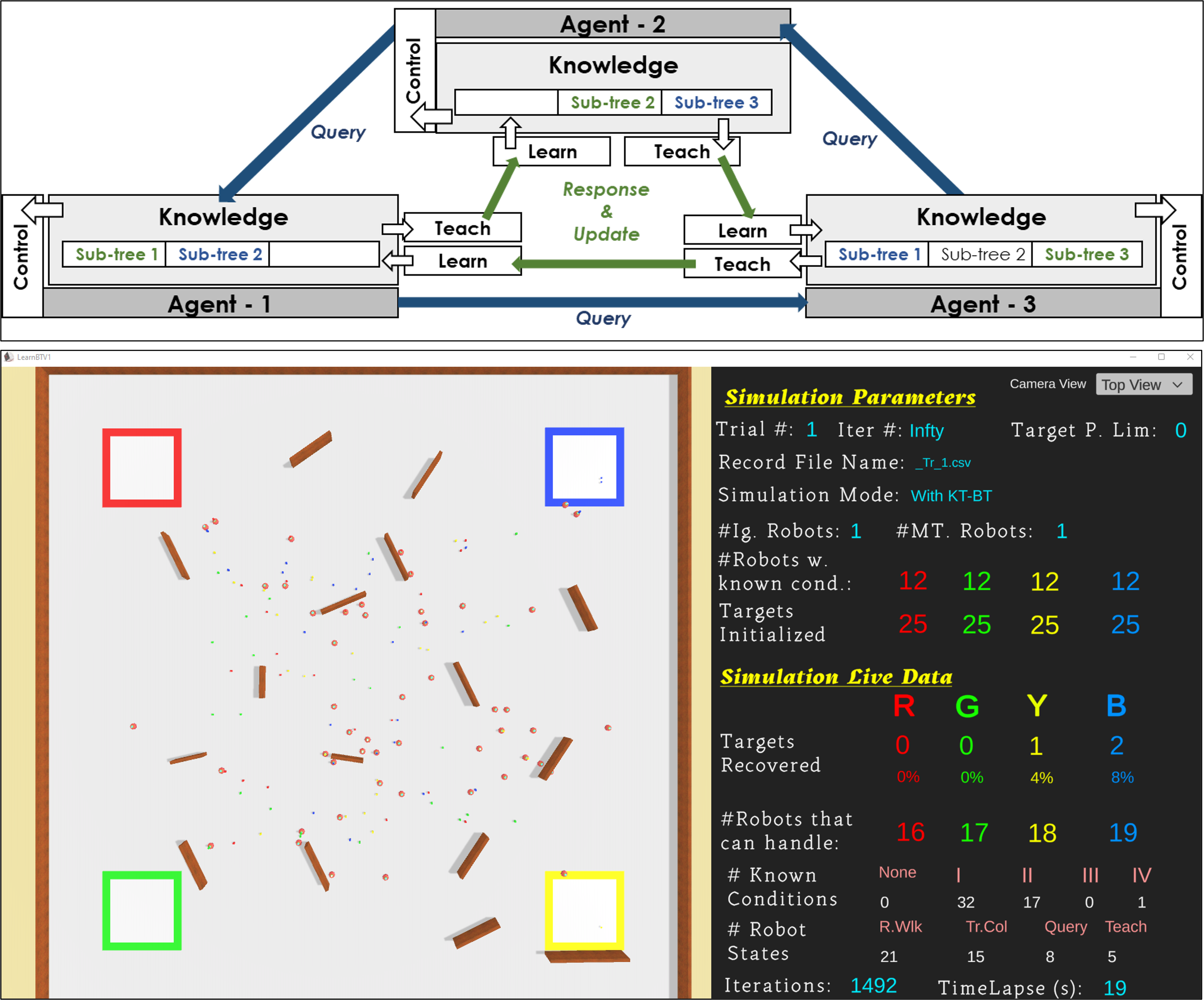
The project focused on enhancing knowledge sharing in multi-robot and multi-agent systems through the development of a novel framework called Knowledge Transfer through Behavior Trees (KT-BT). In heterogeneous multi-robot systems (HMRS), the ability of agents to share knowledge about missions and environments is crucial for improving performance and achieving collective intelligence. However, a generic framework for efficiently transferring knowledge between agents has been lacking.
KT-BT addresses this need by employing a query-response-update mechanism within an online Behavior Tree framework, allowing agents to broadcast queries for unknown conditions and respond with the appropriate knowledge. The framework's novel stringBT grammar structure encodes knowledge, enabling efficient behavior sharing.
Extensive simulations in a multi-robot search and rescue scenario demonstrated successful knowledge transfers and improved group performance. Additionally, the framework explored the effects of communication range and opportunities on group performance, knowledge spread, and functional heterogeneity, providing valuable insights into the dynamics of collective intelligence in robotic systems.